|
CONTENTS
|
| Forum on Caste &
the Tamil Nation |
| Old Habits Die
Very Hard - India's Ugly Underbelly - Badri
Raina "India's
Tamilians have always considered themselves a
distinct race. Distinct from the Aryans who,
history tells us, displaced their Dravidian
ancestors after the conquest of the Indus-Valley
civilizations. The Tamil language and script are
perhaps of greater antiquity than Sanskrit and have
remained largely free of its influence. Not to
speak of Tamil literature which may be the richest
India has to offer, both in depth and scope. Which
is why Tamilians break into passionate protest when
any Tamilian anywhere be perceived as being under
siege. Sri Lanka offering a prime example, as well
as the situation of Tamilians in Malysia. So,
would it be right to infer that Tamilian
civilizational homogeneity brooks no breach?
Wrong..." more |
| How votes are 'caste' in
Tamil Nadu - Joe A Scaria, Economic Times, 13
May 2009 |
Genetic study of Dravidian castes of
Tamil Nadu
S. Kanthimathi, M.Vijaya, and A. Ramesh,
Journal of Genetic Studies, August 2008 |
| Dalits of Tamil Nadu - Sathianathan
Clarke "If we go by the updated 1991 census
records of Tamilnadu, which places the State Dalit
population at 10,712,266 in a total Tamilnadu
population of 55,858,946, a conservative estimate
would put the Paraiyars population at about 6.32
million." |
| So called
'Other Backward Classes' (OBCs) - The Real
Perpetrators of Crime Against
Dalits |
| Dalits of Sri Lanka: Caste-Blind does not
mean casteless - International Dalit Solidarity
Network |
|
On the Unintended Influence of
Janinism on the Development of Caste in Post
Classical Tamil Society - Sudalaimuthu Palaniappan "..Like any other
human being, the average Tamil also functions at
the intersection of many overlapping identities.
In spite of the persistence of a linguistic
identity over two millennia, and a self-conscious
Tamil nationalist political movement of the 20th
century which argued against caste differences
among Tamils, for many Tamils of today, caste is
a significant, if not the primary, identity
still. One of the results of this caste identity
is that many Tamils who are members of the
Scheduled Castes or Dalits feel alienated from
the interests of the Tamil Nationalist
movement."
|
Fuzzy and Neutrosophic
Analysis of Periyar�s Views
on Untouchability - W. B. Vasantha Kandasamy,
Florentin Smarandache, K. Kandasamy |
| Caste & tamilnation.org -
Comment by Dr.S.Ranganathan and
Response by tamilnation.org, June
2006 |
| Are Brahmins
the Dalits of today? -
Francois Gautier, 23 May
2006 |
| On Dalit Phobia -
Chandra Babu Prasad, June 2006 |
| Castes & Caste Observances amongst
Tamils in Ceylon, Rev James Cartman,
1957 |
| Aryan & Tamils - Swami
Vivekananda |
Untouchability and
Catholicism:
The Case of the Paraiyars in South India -
Robert Deli�ge, 1998 |
| The Pattern of Abuse: Southern
District Clashes in Tamil Nadu - Human Rights
Watch Report, 1999 |
| Dalit
Anti-Dravidianism Debunked - Exposing the New
Brahmanic Conspiracy - Mukesh Paswan, 2000 |
| Fundamental genomic
unity of ethnic India is revealed by analysis of
mitochondrial DNA - Research Article, Current
Science, November 200 "...Pallar community
shows a higher frequency of haplogroup-M in DNA
where as North Indian castes show higher frequency
of haplogroup-U meaning that higher Caucasoid
mixture in North Indian castes.Haplogroup-M is
attributed to Dravidians.." |
| Ambedkar |
| Infantry Regiments of Indian Army
& Caste "... Between 1892 and 1914,
recruitment was confined almost entirely to the
martial races. These modes of recruitment and
organization created a professional force
profoundly shaped by caste and regional factors
and loyal and responsive to British command. The
procedures also perpetuated regional and communal
ties and produced an army that was not nationally
based. .." |
| Translating Tamil Dalit Poetry -
Anushiya Sivanarayanan, May 2004 |
| Dalit Panthers of India Leader T
Tirumavalavan visits Jaffna to salute Tamil
Eelam, December 2004 "I want a Tamil
Government... I want a Tamil country... That
country I dream of is coming up in Sri Lanka's
Jaffna. I went there to salute that
land.." |
|
Brahmins & Eelamists, - V.Thangavelu, 2001
"...If not for the social revolution engineered by
Periyar the Tamils would still be hewers of wood
and drawers of water for the master race. ..Is it a
coincidence that the Brahmins are ganging up
against Tamil Nationalism? They oppose Tamil Eelam;
they oppose Tamil as the language of education in
LKG and UKG. Why? Brahmin students offer Sanskrit
as one of the subject for Plus 11 instead of Tamil.
Why? .." |
| Pfaffenberger, Bryan -
Caste in Tamil Culture:
The Religious Foundations of Sudra Domination in
Tamil Sri Lanka, Syracuse, Syracuse University,
1982. |
| Nature of Caste in Sri Lanka
"When the Portuguese
began to trade extensively with South Asia, they
quickly noticed a fundamental difference between
South Asian societies and those of other world
areas. In India and Sri Lanka, societies are broken
up into a large number of groups who do not
intermarry, who are ranked in relation to each
other, and whose interactions are governed by a
multitude of ritualized behaviors. The Portuguese
called these groups casta, from which the
English term caste is derived. In South
Asia, they are described by the term jati,
or birth. According to traditional culture, every
person is born into a particular group that defines
his or her unchangeable position within
society." |
| தலித்
இலக்கியம்
- Thamizh Arasan -
அடங்க
மறு |
| Caste & The Myth of Hindu
Tolerance |
| Caste in
Ceylon - Country Study |
| Forum - Who is a Tamil? |
| On Origin of
Pallars at Forum Hub |
| Tamil Nadu: shaking off the shackles of
Hindu caste, 2002 |
| Implementation of
Social Justice Through Reservation -Dr. Justice P.
Venugopal |
| Caste in
Wikpedia |
| Shudras-
Untouchables- Dalits at Asian Human
Rights |
| Why Dalits
dont Need Brahmins |
| Dalits In Reverse "... From
being the dominant community at one time, the Tamil
Brahmins are facing the effects of a new
casteism.." |
| Needed A
Tsunami To Destroy The Ugly Relic Of Varna
System - V.B.Rawat,
2005 |
| Dwelling in Futures
Past: Place, Region and Tamil Nation in Ra.
Krsnamurti�s Civakamiyin
Capatam - Akhila
Ramnarayan |
| Vedic "Aryans"
and the Origins of Civilization: A Literary and
Scientific Perspective - Navaratna S.
Rajaram and Davis Frawley. |
| Caste and
Religions of Natal Immigrants
- K. Chetty |
|
Caste in
Transition - V.G. Julie Rajan
2003
Caste,
nationalism, and ethnicity : an interpretation of
Tamil cultural history and social order -
Jacob Pandian
|
| National Campaign on
Dalit Human Rights |
| Tamils group seen exploiting
caste in Jaffna election, 1998 |
| Danger Stalks
Dalit Leaders, 2004 |
| Dalits in
Dravidian Land, 2005 |

Visit Tamil Nation
Library
- Caste & Tamil Nation |
|
Caste &
the Tamil Nation -
Dalits, Brahmins & Non Brahmins
"The
Tamil nation is a political community, a
grand solidarity. To maintain its solidarity,
the Tamil nation has to remove all sorts of
divisions that causes dissension and discord
among its members. The Caste System is such a
pernicious division that has plagued our society
for thousands of years." S.M.Lingam on Tamil Nationalism & the
Caste System - Swami Vivekananda and Saint
Kabir
�Day in and day out we
take pride in claiming that India has a 5000 year
old civilization. But the way Dalits and those
suppressed are being treated by the people who
wield power and authority speaks volumes for the
degradations of our moral structure and civilized
standards.� Ex-President of
India, the late K. R. Narayanan, The New Indian
Express, Saturday, 12 Nov. 2005 quoted in
Fuzzy
and Neutrosophic Analysis of
Periyar�s Views on
Untouchability - Dr.W. B. Vasantha Kandasamy,
Dr.Florentin Smarandache, & Dr.K.
Kandasamy
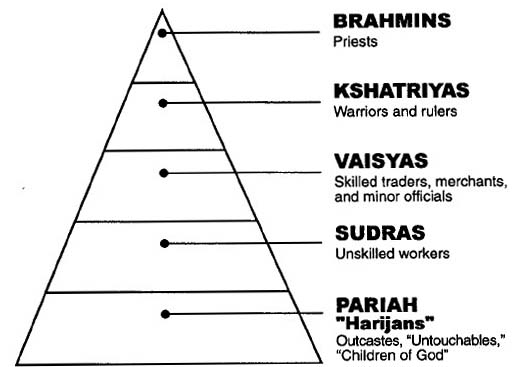
"...The caste
system of South India, epitomized (as are most
things South Indian) by the social formation of
the Tamil-speaking lands is if anything even more
rigid and redolent of the hierarchical ethos than
that of North India. And yet - here, of course,
is the uniquitous paradox with which South Indian
presents us - the Tamil caste system comprises
features which are not only unknown in North
India but are also without any clear foundation
in the Sastric lore. So divergent is the
southern system that one is tempted to say, with
Raghavan (n.d.:117), that the Sastras have
"little application" to the Tamil caste system,
which should be analyzed in purely Dravidian
terms...But to do so is to forget the fundamental
challenge with which Dravidian culture presents
us, namely, to see it as a regional variant of
the Gangetic tradition of Hinduism. We are
obliged to observe, for instance, that the
highest and lowest ranks of the Tamil caste
hierarchy - that of the Brahman and of the
scavenging Paraiyar Untouchables -are perfectly
explicable in Sastric terms. ..
To argue that the Sastric
ranking ideology has "little application" to the
Tamil caste system is to ignore the challenge
that South India presents to ethnology. Yet it is
also true that, in the middle ranges of the Tamil
caste hierarchy, the ranking categories and
overall form of the Gangetic caste tradition are
very poorly reproduced.
The most
striking aspect of this anomaly is the enigmatic
status of certain non-Brahman cultivating castes,
which are traditionally of the Sudra (or Servant)
rank in Sastric terms and which are epitomized by
the cultivating Vellalars of the Tamil
hinterland. Throughout South India, in those
areas in which Brahmans are not the chief
landowners, Sudra cultivating castes often
possess what Srinivas has termed "decisive
dominance"" Caste in Tamil Culture: The Religious
Foundations of Sudra Domination in Tamil Sri
Lanka, Bryan
Pfaffenberger
|
|

The Stink of
Untouchability
|
1. S.M.Lingam on Tamil Nationalism &
the Caste System - Swami Vivekananda and Saint
Kabir
"The Tamil nation is a political
community, a grand solidarity. To maintain its
solidarity, the Tamil nation has to remove all
sorts of divisions that causes dissension and
discord among its members. The Caste System
is such a pernicious division that has plagued
our society for thousands of years.
The Caste System still occupies an important
place in the Hindu religion. The primary aim and
ideal of all religions is the emancipation of all
its followers, especially that of the weaker
sections and the downtrodden. So it is strange
that a religion like Hinduism goes against that
ideal and purposefully condemn a section of its
own followers as untouchable outcasts. The Hindu
Brahmins have created theoretical explanations,
Puranic stories and religious myths to support
and justify their conduct. The sole aim of what
is called "Brahminism" is to create and maintain
a system which gives a supreme place of
importance to Brahmanic priests and other
Brahmins in general. Since all of these arguments
are purported to be based on Hinduism, it is
proper that we examine the ideals of real Hinduism and its
basic tenets. .." more
|
6. Professor Hart in Forum
on Brahminism & the Tamil Nation
"..Yes, of course Brahmins have had their own
political agenda to push. They have been
responsible for many things that I feel are
entirely unconscionable. But is this any
different from the other high castes? I have
heard many many stories of high non-Brahmin
castes killing and abusing Dalits. You can't
blame the Brahmins for this. In fact, the most
pernicious example of the caste system was in the
Tamil areas of Sri Lanka, where there are
virtually no Brahmins and never have
been....Tamil culture has not suffered because of
one group. It has suffered because of the caste
system and because of its treatment of
women... Let's promote inter caste marriage,
let's get rid of dowry and give
women independence and self-respect, and above
all, let's avoid a victimization complex which
only plays into the hands of those who have a
vested interest in continuing the inequities that
exist in Tamilnad. If every Brahmin were to
disappear from Tamilnad, the Dalits and others
who are exploited would benefited not one
iota..."
|
3. Sanmugam Sabesan
- சாதி ..
"�சாதியம்
என்பது
மனித
குலத்திற்கு
எதிரானது.
அடிப்படை
மனித
உரிமை
மீறலாகும்.�
என்று
ஐக்கிய
நாடுகள்
சபைக்கு
பரிந்துரை
செய்யப்பட்டுள்ளது.
இதனை
நாமும்
முழுமையாக
வரவேற்கின்றோம்
நான்கு
வருண
உருவாக்கம்
குறித்துப்
பேசுகின்ற
�இருக்கு
வேதத்தின்�
புருஷ
சூக்தத்தில்,
புருஷன்
என்கின்ற
உடலை
நான்காக
வகுத்து
நான்கு
வருணங்கள்
தோற்றுவிக்கப்
பட்டதாகக்
கதையாடல்
அமைக்கப்
பட்டுள்ளது.
படைப்புக்
கடவுள்
பிரம்மாவின்
வாயிலிருந்து
பிராமணனும்,
நெஞ்சில்
இருந்து
சத்திரியனும்,
தொடையிலிருந்து
வைசியனும்,
பாதத்திலிருந்து
இவர்கள்
மூவருக்கும்
சேவை
செய்யும்
அடிமையாக
சூத்திரன்
என்பவனும்
உருவாக்கப்
பட்டார்கள்.
இந்த
சூத்திர
சாதியை
சேர்ந்தவர்கள்தான்
திராவிடர்கள்
என்பது
பின்னால்
விளக்கப்
படுகின்றது.
இந்த
நான்கு
வருணத்தையும்
(நான்கு
சாதி
அமைப்புக்களையும்)
தாண்டியவர்கள்
மிகக்
கேவலமாக
சண்டாளர்கள்-
தீண்டத்
தகாதவர்கள்
என
அழைக்கப்பட்டு,
ஒதுக்கப்பட்டு,
ஒதுக்கப்படுகின்றார்கள்.
இவர்கள்
�தலித்துக்கள்�
என்று
இப்போது
குறிக்கப்
படுகின்றார்கள்.
�தலித்�
என்ற
சொல்
எப்படி
வந்தது
என்பதை
முதலில்
பார்ப்போம்..."
more
|
|
4. 'In the rainy season,' the woman
began, `it is really bad. Water mixes with the shit
and when we carry it (on our heads) it drips from
the baskets, on to our clothes, our bodies, our
faces. When I return home I find it difficult to
eat food sometimes. The smell never gets out of my
clothes, my hair. But this is our fate. To feed my
children I have no option but to do this work.'
Narayanamma began cleaning human
excrement at 13. She is now 35. The stench is
nauseating, overpowering. First, she sweeps the
shit into piles. Then, using two flat pieces of
tin, she scoops it up and drops it into a bamboo
basket which she carries to a spot where a tractor
will arrive to pick it up. No gloves. No water to
wash with. She hitches up her sari tightly so that
it does not trail on the ground or touch the shit.
Still, it is almost impossible to go through a
whole day's work without some of it inadvertently
getting onto her clothes and person.
After 20-odd years of cleaning
toilets. Narayanamma clings to a dignity which is
markedly at variance with the work she does. She is
dressed neatly, immaculately clean. Jasmine adorns
her oiled and well groomed hair.
Narayanamma and 800,000 other
toilet cleaners are on the lowest rung of the caste
system in India. They are despised by everyone.
They experience absolute exclusion from the cradle
to the grave.
They are the other face of
India; the one that nobody likes to see. It is in
sharp contrast to the progressive, technological,
we-have-the-bomb-and-are-no
longer-the-Third-World face.
Chennai railway, station says it
all. It has a hot spot for laptops to download
mail, mobile phone chargers, international food
counters offering burgers, chocolate mousse and
chow mein next to hot dosas and chicken tikka.
Yet, a few metres away, sweeper women clean shit
in the most primitive manner possible, lifting it
out of the railway track with a stick, broom and
pieces of tin. Why does this unacceptable,
utterly obscene dichotomy exist. Because hardly
anyone wants it to change.
Caste permeates every pore of
Indian society in hidden, insidious ways. It is so
complex, few Indians begin to understand it
completely, although it is present in our lives in
subtle and not-so subtle ways. Even though the
caste hierarchy is a Hindu construct, conversion
does not always help: Buddhists, Christians, Sikhs
and Muslims often still cling to their caste
identities when searching for marriage
partners...
When the British ruled India they
left caste well alone to avoid unrest. In some ways
they even reinforced it, finding Brahmins useful as
an army of clerks and administrators who served the
British Empire faithfully.
Today, in India, the Untouchables
call themselves `Dalits', which means `Broken
People'. There are almost 180 million Dalits in
India alone and at least another 60 million around
the world who face caste discrimination of various
kinds.
On a daily basis, Dalits have to
deal with the fact that they will not be served
food in many eateries. They must sit outside and
drink their tea at a distance from the other
customers. Special `Untouchable' cups are placed on
the shelf outside. The Dalit customer has to take
his or her cup, place it on a counter carefully
without touching the waiter. The tea will then be
poured from a safe, non polluting distance and the
Dalit must pick up the cup, drink the tea, wash the
cup and place it back on the secluded Dalit shelf
outside. This is known as the 'two-glass'
system.
In one recent survey of 22 villages
in Tamil Nadu, 16 practised the `two glass system';
14 villages had the `chappal' system where Dalits
have to remove their footwear when they enter the
caste part of the village; and in 17 villages
Dalits were forbidden to enter the village temples.
In four villages Dalits had come together to combat
these practices and they have largely been
abolished....
... Academics talk of lack of
political will to describe successive
governments' failure to protect Dalits.
Translated, this means police officers stand in
the background and watch upper-caste mobs burn
Dalits alive, because the village considers they
are getting too big for their boots. Feudal
landlords are aided by corrupt civil servants and
government officials in maintaining the status
quo. So they approve and abet in the exploitation
of Dalits, turn a blind eye to bonded labour, and
the terrorizing, killing, rape of Dalits who
protest. Meanwhile everyone mouths the rhetoric
of the Constitution and government documents
hypocritically pay lip-service to it...
Caste discrimination also remains
alive and well wherever the Indian Diaspora has
migrated.. ...Perversely caste discrimination in
Diaspora communities in the West has become worse
in the last few years; as communities have grown
larger, caste distinctions become more
pronounced...
Discrimination in Detail
-
In India, Brahmins, who
are 3.5 per cent of the population, hold 78
per cent of the judicial positions and
approximately 50 per cent of parliamentary
seats.
-
Mass rapes often form part of
the tactics of intimidation used by
upper-caste gangs against lower castes. The
Home Ministry reported that, between 2000 and
2001, there was a 16.5 per cent increase in
reported rape cases.
-
Each year, inter-caste
violence claims hundreds of lives; in 2001 it
was especially pronounced in Uttar Pradesh,
Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil
Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh.
-
In India, among the millions
of bonded labourers (estimates range widely
between 20 to 65 million for 2001), the
Government found 85 per cent to be Dalits or
from lower castes. These included a large
number of children.
-
Dalits and adivasis
(indigenous peoples) form the largest
proportion of those who drop out of school.
In rural areas, between the ages of five and
nine, 36.1 per cent of Dalit boys and 48.4
per cent of Dalit girls dropped out.
-
About 75 per cent of Dalit
communities live below the poverty line.
-
Two-thirds of the Dalit
population is illiterate.
-
Half are landless
agricultural labourers.
-
Only seven per cent have
access to safe drinking water, electricity
and toilets.
from Mari Marcel Thekaekara on
the Stink of Untouchability in the
New
Internationalist, July 2005
|
5. Untouchability & Caste Relations
in Rural India - the Case of Southern Tamil
Villages - A. Ramaiah
"Justice and equality are the two subjects
often talked about by most of the nationalists
and leaders of various political and ideological
streams across the world including
India....everyday social life is still governed
substantially by the hierarchical attitude and
sentiments carried over from the past. The awe
for those who are superior by birth or social
position (higher caste) and the contempt towards
social inferiors (lower castes) are equally wide
spread in the rural and urban areas and among the
educated and the uneducated... What is most
important of all is reconsidering the suggestion
of Dr. Ambedkar that a socially distinct
community should be allowed to settle in separate
villages so that within such villages there is no
scope for any one to label another as untouchable
or lower caste. Only in such separate villages
can the so-called lower caste people also
experience freedom which India got five decades
before. Besides, a fire spewing urge to fight for
their rights, self-respect and dignity and a
strive for coming together across their
religious, regional, linguistic, sub-caste and
ideological differences have to be consciously
nurtured. Unless this is achieved, the
empowerment and the emancipation of enslaved
Indians would continue to remain a distant
dream.� more
|
6. Pfaffenberger, Bryan -
Caste in Tamil Culture: The Religious Foundations
of Sudra Domination in Tamil Sri Lanka
"...The caste system of South India,
epitomized (as are most things South Indian) by
the social formation of the Tamil-speaking lands
is if anything even more rigid and redolent of
the hierarchical ethos than that of North India.
And yet - here, of course, is the uniquitous
paradox with which South Indian presents us - the
Tamil caste system comprises features which are
not only unknown in North India but are also
without any clear foundation in the Sastric lore.
So divergent is the southern system that one is
tempted to say, with Raghavan (n.d.:117), that
the Sastras have "little application" to the
Tamil caste system, which should be analyzed in
purely Dravidian terms...But to do so is to
forget the fundamental challenge with which
Dravidian culture presents us, namely, to see it
as a regional variant of the Gangetic tradition
of Hinduism. We are obliged to observe, for
instance, that the highest and lowest ranks of
the Tamil caste hierarchy - that of the Brahman
and of the scavenging Paraiyar Untouchables -are
perfectly explicable in Sastric terms. .."
more
|
7..K.Nambi Arooran in The Origin of the
Non-Brahmin Movement, 1905-1920
".. although non Brahmins from the two main
Dravidian language groups - Tamil and Telegu -
joined the non-Brahmin movement the use of
Dravidianism as a political weapon was mostly
confined to the Tamil non-Brahmins... At the same
time when Dravidian consciousness was taking
shape not only the question who were Dravidians
but also the question who were non-Brahmins came
to be widely asked. The leaders of the Justice
Party claimed that the term ` non-Brahmins'
denoted all other than ` Brahmins'. But the
leadership of the party came mostly from the `
advanced ' or ` forward ' non-Brahmin Hindu
castes which according to one estimate formed
about 19 per cent of the population."
|
8.
Nadesan Satyendra in the Tamil Heritage
"...in the end, Periyar E.V.Ramasamy, the
undoubted father of the Dravidian movement failed
to deliver on the promise of Dravida Nadu. E.V.R.
failed where Mohamed Ali Jinnah succeeded. It is
true that the strategic considerations of the
ruling colonial power were different in each case
- and this had something to do with
Jinnah�s success. But,
nevertheless, if ideology is concerned with
moving a people to action, the question may well
be asked: why did E.V.R�s
ideology fail to deliver Dravida Nadu?... Support
for the positive contributions that E.V.R. made
in the area of social reform and to rational
thought, should not prevent an examination of
where it was that he went wrong. Again, it may
well be that E.V.R. represented a necessary phase
in the struggle of the Tamil people and given the
objective conditions of the 1920s and 1930s,
E.V.R was right to focus sharply on the immediate
contradiction posed by 'upper' caste dominance
and mooda nambikai. But in the 21st century,
there may be a need to learn from E.V.R. - and
not simply repeat that which he said or
did..."
|
9. திராவிடக்
கட்சிகளின்
தமிழ்த்
தேசியம்
- Sanmugam Sabesan, 2005
�திராவிடன்
என்ற
மரபு
இனத்தை
தி.மு.க
முன்
வைத்தது,
தமிழ்த்
தேசியக்
கோட்பாட்டிற்குப்
புறம்பான
நிலைப்பாடு.
தமிழன்
என்ற
தேசிய
இனத்தை
மட்டும்
முன்
வைத்திருக்க
வேண்டும்.
அது
மட்டுமல்ல
பிற்காலத்தில்
இக்கழகம்
நாட்டால்
இந்தியன்,
இனத்தால்
திராவிடன்,
மொழியால்
தமிழன்
என்று
கூறிக்
கொள்ளத்
தொடங்கியது.
இது
தேசிய
இனவரையறைக்குப்
புறம்பான
உளறல்
மட்டுமல்ல,
தமிழ்த்
தேசியத்தை
ஊனப்படுத்தும்
போக்கும்
ஆகும்.�
more
|
10.Dravidian Movement & Dalits -
Gail Omvedt ...
"In Tamil Nadu there was a movement in the
name of anti-Brahmanism under the leadership of
Periyar. It attracted Dalits, but
after 30 years of power, the Dalits understand
that they are as badly-off - or worse-off - as
they were under the Brahmans. Under Dravidian
rule, they have been attacked and killed, their
due share in government service is not given,
they are not allowed to rise.'' So says Dr.
Krishnasami, leader of the militant movement of
the Dalit community known as ``Devendra Kula
Vellalas'' of southern Tamil Nadu and founder of
a new political party, Puthiya Tamilakam. This
sense of disillusionment with the Dravidian
parties is pervasive among not only the Dalits
but also many militant non-Brahmans as well. The
anti-caste movements of the past, in Dr.
Krishnasami's words, have failed to achieve their
main goals. Mr. Thirumavalavan of the
Liberation Panthers speaks of discrimination and
atrocities against those who fight against the
evil and adds: ``Castes keep their identity just
as before, they don't intermarry, there are no
longer any self-respect marriages.''
Like Dr. Krishnasami, he does not reject the
goals of the movement, arguing ``the Dalit
struggle has to be for the liberation of a
nationality,'' and Hindutva should be opposed
through Tamil nationalism. He feels that
the existing Dravidian parties have betrayed the
Dalits."
|
11.On
Hinduism, Caste, & Indian 'Democracy' -
Dr.Iniyan Elango, 1999
"..Hinduism espouses the
division of people into hierarchically placed
groups called
�castes�. These
castes are placed in a stepladder of ascending
superiority and descending inferiority. People
who are born into these castes should follow the
ordained caste professions and marry only within
their caste through arranged marriages. The
beneficiaries of this system were the various
Brahman castes who by virtue of their birth were
free to follow intellectual pursuits at the
advent of British colonial education making them
modern India�s intellectual,
scientific, and bureaucratic class. The various
�Vysya�
(trading) castes, placed below the Brahman castes
and the Royal
(�Kshatriya�)
castes, have enjoyed the monopoly in trading
activities for centuries, by virtue of their
birth, thus becoming modern
India�s corporate and business
class. The
�Shudras� are
the various lower castes in the hierarchy who are
considered as Hindus and members of caste Hindu
society...Rape is the most common risk faced by a
Dalit woman in the Hindu society. The English
language dictionary even now carries the word
"Pariah" (which is the Tamil name for the large
population of Dalits living in Tamil Nadu in
India) to convey the meaning of "outcast". "
|
12. Racial Origin of Caste
-Senthil Veliappa
"...The Vedic system of apartheid is one of
the most dehumanizing on record. Some Vaishnava
apologists refuse to believe that caste is racial
in origin, and claim that it is due to
profession. Such people also claim that
`conversion' to Hinduism is allowed and that a
person of one caste can become a person of
another caste. This arises due to their
deliberate confusion of two distinct terms,
`varna' or race, and `jati' or professional
guild. The fact is that `varna' in Sanskrit
denotes skin color, and implies race, while
`jati' is the professional guild which a person
belongs to.."
|
13. Towards a Non Brahmin
Millenium - V.Geeta, S.V..Rajadurai
"..In a context when
Brahmins claimed that birth was no more a badge
of status and then went ahead to act and speak as
if it was, non-Brahmins, comprising a range of
castes and communities, including both those who
owned land and those who laboured on it, claimed
the contrary. They called attention to practices
of discrimination, humiliation and negation
suffered on account of their always already lowly
birth, and came to articulate a philosophy and
practice of rights which would help them combat
inequality and humiliation..."
|
|
14. Adheedhan Ravikumar on Iyothee
Thass & The Politics of Naming, August
2005
On 3 September, Prime Minister
Manmohan Singh is all set to inaugurate National
Center for Siddha Research in Chennai. The
research centre was originally to be named after
Pandit C. Iyothee Thass (1845-1914), a renowned
practitioner of the Siddha form of native Tamil
medicine, and also a pioneer of the Tamil Dalit
movement. However, the name of Iyothee Thass has
been dropped. The foundation for the project was
laid on March 27, 1999 by the then Tamil Nadu
chief minister M. Karunanidhi in the presence of
then Union Health Minister, Dalit Ezhilmalai, of
the Pattali Makkal Katchi (PMK). It was at the
behest of Dalit Ezhilmalai that the institute was
named after Iyothee Thass.
After seven years, Iyothee
Thass's name does not figure anywhere. Dalit
organizations are protesting. Se. Ku. Tamilarasan
of the Republican Party of India (RPI), a sitting
MLA, has announced a black flag demonstration
against the prime minister and union health
minister Anbumani Ramadoss if they refuse to name
the institute after the Dalit leader.
The last decade of 20th century
marks a significant chapter in the history of
Tamil Nadu as the Dalits waged a fearless war
against the shudra repression in the
sociopolitical realm. The caste war which started
in the southern districts slowly spread to the
northern districts. The Vanniars designated a
Most Backward Class were the main perpetrators of
atrocities against dalits in the northern
districts. To take the sting off allegations of
being casteist and anti-Dalit, the PMK, a party
of Vanniars, made Dalit Ezhilmalai a Union
minister in the BJP-led government. Within a
year, Ezhilmalai demonstrated that he had a mind
of his own and started functioning independent of
his political masters. It was during Ezhilmalai's
ministership and with his patronage that a
section of Tamil Dalits rediscovered Iyothee
Thass.
The Dalit thinker's writings were
reprinted in five volumes through a publishing
house called Dalit Sahitya Academy owned by
Ezhilmalai. Thass emerged as an icon of Dalit
assertion in the ideological sphere. Though the
medical knowledge of Iyothee Thass was recognized
by many of his contemporaries, including Colonel
Henry Steel Olcott of the Theosophical Society
and Thiru. Vi. Kalyasasundaram, a famous Tamil
scholar, the attempt made by Dalit Ezhilmalai to
name the Siddha research institute after him must
be understood in the context of the political
assertion of dalits in the 1990s.
Iyothee Thass is perhaps one
among the several Dalit icons whose names have
been blacked out by mainstream history. ..
more
|
15. Early Evidence of Caste in South India -
George L.Hart
"At first glance, caste seems a phenomenon
which, if not simple, is at least amenable to
explanation and description; yet, as the vast
number of writings on the subject and their many
different points of view indicate, this is not
the case...The modern form of the caste system
seems to have been the result of changes
introduced by the Brahmins and by kings who
fostered the Hindu system...As important as the
Brahmins and the Brahmanical religion were, they
were not the creators of the caste system in
South India. They influenced the system
profoundly, no doubt, but caste is found in most
of its manifestations before the Brahmins became
prominent. Its origins must be seen in the belief
system that developed with the agricultural
civilization of South India: that sacred power in
its natural state is dangerous and demands groups
outside of society proper to control it. .."
|
16..Rise of Caste in Dravida Land
"...the DMK did keep the plank of cultural
nationalism alive until the killing of Rajiv
Gandhi in Sriperumbudur. Ever since, the spectre
of Tamil nationalism evokes the ghosts of
Sivarasan and Dhanu, the suicide bombers of the
LTTE. The cracking up of the anti-Brahmin
umbrella happened alongside the decline of
cultural nationalism as an emotional issue in
Tamil Nadu. Improved literacy and decline in the
number of poor brought to the fore new political
and economic aspirations. The success of Vanniyar
Sanghom, and later its political outfit, the
Pattali Makkal Katchi, was an eye opener to
others on power play.
The emergence of an educated class among Dalits -
Pallars in the south and Parayars in central
Tamil Nadu - has led to caste consolidation in
these areas. The riots during the mid-90s have
polarised Dalits and dominant OBC groups
including the Thevars leading to the emergence of
vote blocks. Various elections since 1996 have
demonstrated that these vote blocks can decide
poll outcomes. The DMK and the AIADMK had no
option but to agree to accommodate the new
interests if they were serious about winning
elections... Alliterative oratory punctuated with
gems from classical texts will not be able to
match the arithmetic of castes..."
|
17.
The Legend of Nandan: Nandan Kathai - Indira
Parthasarathy , 2003
"Accounting for over 80 per cent of the
landless agricultural workers and doing menial
jobs for the rest of society, Dalits have been
victims of class-related economic exploitation by
upper-caste landholders. Contrary to the
expectations generated among people during the
freedom struggle, Independence has not brought
any significant change in their lives. Dalits'
attempts at upward mobility are often scorned and
there has been no let-up in the violence against
them. In a gruesome incident that took place at
East Venmani in Tamil Nadu's Thanjavur district
on December 25, 1968, 44 Dalit agricultural
workers, including women and children, were burnt
alive by the land-owners of the village because
they demanded higher wages.."
|
18. Dalits at the Indian Institutes
of Technology
"Nandanar, a dalit rebel-activist of the
bhakti period, sought access to the
Shivaloganadar temple in Tiruppungur and the
Nataraja temple in Chidambaram, to which the
'untouchable' Pulaiyars provided hereditary
services (supplying leather for percussion
instruments). For this, the Brahman clergy
derided him. The Tamil saivite tradition went on
to appropriate the political resistance of
Nandanar in the great Hindu habit of
'assimilation'. In Sekkizhar's Peiryapuranam, a
12th century saivite hagiography, the dalit
martyr is made to undergo a 'conversion' - he
gains access to worship only after his
caste-oppressed pulaiya body is 'purified' by the
sacrificial fire, and lo! he emerges as a Brahman
sage - tuft, caste thread, and all. Siva is shown
to accept the dalit after he undergoes a
trial-by-fire. In reality, Nandanar was burnt to
death. Incinerated. Today, many dalit students at
the Indian Institutes of Technology have to
survive a 'Preparatory Course' fire and come out
unscathed if they have to do B. Tech. Not much
has changed. The dalits fought for temple-entry;
today they fight for entry into IITs - temples of
technology..."
|
|
see also Forum
on Caste & the Tamil Nation....
|
|